 ERASPAAS - Internet of Things
ERASPAAS - Internet of Things ERASPAAS - Internet of Things
ERASPAAS - Internet of Things2.5.1 Filter / Filter Operator
2.5.2 Condition / Condition Operator / Condition Server Value
This document details on Eraspaas Application Program Interface (API), and how the different actions can be performed programmatically through action service. The web service for performing actions in an Eraspaas domain is available over standard web API, both SOAP and REST, accepting data in XML or JSON format. This ability to perform the actions through different endpoints allows all possible platforms and programming language to interact with Eraspaas platform.
The Eraspaas action service provides a consistent interface for invoking the actions, effectively making it easy and intuitive to call the service for performing different actions. So by learning how to call a single action enables one to be able to perform the different actions just by knowing the parameters (fields) expected by the respective action.
In the interest of keeping the document precise, pseudo code samples are provided that can be easily adopted for JAVA, .Net, PHP, JavaScript or Objective-C. While both JAVA and .Net can conveniently consume the service through SOAP endpoint, other languages would find REST endpoint with JSON data format as more straightforward and efficient.
The endpoint addresses:-
SOAP base address – http://eras.in/Host/
REST base address – http://eras.in/Host/service/perform
Note: the base endpoint address provides the minimal set actions that will be compatible with all future versions of the platform service. This includes all standard actions such as CreateRecord, UpdateRecord, DeleteRecord, ImportData, ExportData, UploadAttachment, etc.; (as detailed in this document). However while developing application which wants to leverage actions introduced in subsequent Eraspaas platform service releases then the endpoint address should contain the service version required by the application; as –
SOAP versioned address – http://eras.in/Host/v1.1/
REST versioned address – http://eras.in/Host/v1.1/service/perform
Note: for versioned addresses the concerned Eraspaas domain should have upgraded to the respective required service version or higher.
Besides invoking the host service directly it is also possible to use the handlers at the presentation layer. This approach is particularly advantageous for calls made from JavaScript from sites (html pages) hosted in Eraspaas platform or custom scripts provided as FormScript or ViewScript. When handlers are used from scripts the current logged-in user identity is used for such calls.
For an overview of handlers refer to "Eraspaas Site, Handlers and Reports" document.
The Eraspaas service platform has n-tier architecture and as a framework it is logically organized in MVP architectural pattern.
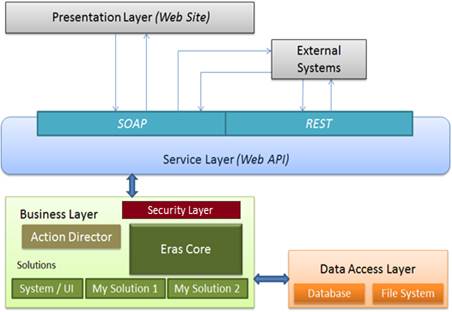
Eraspaas Layered Architecture
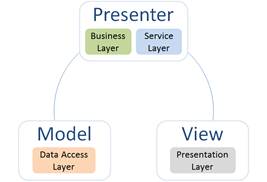
Eraspaas Logical Pattern – Model View Presenter (MVP)
The Action Director manages the sequence of actions that are available in the Eraspaas Core. The Actions are categorised into three types:
i. On Demand Actions: These are actions that are explicitly triggered by user s or applications.
ii. On Event Actions: These are actions that get triggered indirectly as a consequence of some other action.
iii. On Schedule Actions: These are actions are automatically triggered at given time intervals.
Note: Scheduled actions has limited support based on subscription level, however as an alternative it is possible to build applications that trigger actions at desired time intervals.
When a request to perform an action is received by the Eraspaas host service, the action director prepares an execution sequence of On Event Actions that are observing the current action being performed. The sequence of execution is guided by the PerformOrder field value of the On Event Actions. The dependant actions that have perform order less than 0 (zero) are executed before the actual requested action is performed, such actions are referred as pre event actions. While the dependant actions that have perform order greater than 0 (zero) are triggered after requested action is performed. This enables a chain of responsibility to be performed by different actions in the order of configured perform order.
Thus it is possible to plug-in any custom action as a consequence of some other action triggered by the user. For example When the CreateRecord or UpdateRecord action is performed on Entity (System_Entity) corresponding dependant action automatically update or modify the database table structure corresponding to the entity.
The platform is designed to provide a consistent structure for calling any action at the service. The Action Service receives an Action Request object that specifies the Action Name, a Session Id and an Input Record object that has Fields property containing key value pairs of input parameters for the specified action. The Action Service returns Action Response object containing an Output object of any type which is convertible to the type as expected for the given action.
The ActionService (service proxy instance) for calling SOAP endpoint address:
ActionServiceClient _service = new ActionServiceClient();
ActionRequest request = new ActionRequest();
request.ActionName = "NameOfAction";
request.SessionId = "<SessionId returned from Connect action>";
Record input = new Record();
//set record object EntityName and Fields as required by the action
request.Input = input;
ActionResponse response = _service.Perform(request);
//Perform function takes ActionRequest as input and returns ActionResponse
Note: in case of REST JSON request the ActionServiceClient (or ActionServiceProxy) is not required. The JSON corresponding to ActionRequest object is posted to the rest endpoint address which returns the JSON corresponding to ActionResponse as response to the http request.
The ActionRequest object passed to perform operation at the service:
public class ActionRequest
{
public string SessionId { get; set; }
public string ActionName { get; set; }
public Record Input { get; set; }
}
The ActionResponse object returned from perform operation:
public class ActionResponse
{
public string ErrorMessage { get; set; }
public object Output { get; set; }
}
Note as the service performs operation successfully the ErrorMessage field is set to null, only when the service fails to perform operation due to a malformed request the ErrorMessage field contains information about the error.
The input property of request contains a Record object as the input parameter for the action being called.
The Record object structure that is set to Input property of ActionRequest:
public class Record
{
public string EntityName { get; set; }
public string RecordId { get; set; }
public Field[] Fields { get; set; }
}
The Field objects structure that is set in the Record object as Key Value pair (parameters) for the action being performed:
public class Field
{
public string Key { get; set; }
public object Value { get; set; }
}
The same input Record object is also used for querying information from the platform; however the Fields property of the record being passed may contain other complex objects. The RetrieveMultipleRecords andRetrieveViewData actions show how these structures are applied for performing complex queries.
2.5.1 Filter / Filter Operator
The Filter object represents a group of conditions grouped together with a logical "And" or "Or" operator. The Filter object structure passed as field value for a field with key "Filter" in case of Retrieve actions:
public class Filter
{
public FilterOperator Operator { get; set; }
public Condition[] Conditions { get; set; }
public Filter[] SubFilters { get; set; }
}
public enum FilterOperator
{
And = 0,
Or = 1,
}
2.5.2 Condition / Condition Operator / Condition Server Value
The condition object structure passed with filter that specifies the condition as fieldname equals some value:
public class Condition
{
public string FieldName { get; set; }
public bool IsNot { get; set; }
public ConditionOperator Operator { get; set; }
public object[] Values { get; set; }
public ConditionServerValue ServerValue { get; set; }
}
public enum ConditionOperator
{
Equal = 0,
GreaterThan = 1,
LessThan = 2,
GreaterThanEqual = 3,
LessThanEqual = 4,
In = 5,
Between = 6,
IsNull = 7,
On = 8,
OnOrBefore = 9,
OnOrAfter = 10,
ChildOf = 11,
Contains = 12,
BeginsWith = 13,
EndsWith = 14,
IsTrue = 15,
IsFalse = 16,
}
public enum ConditionServerValue
{
None = 0,
CurrentUser = 1,
CurrentDepartment = 2,
CurrentDomain = 3,
CurrentDateTime = 4,
CurrentDate = 5,
}
Notes:
The IsNot property of the condition can be used to reverse the condition.
The Values array would mostly contain single value for most condition operators but for certain condition operators it may contain no values or multiple values. The Values property of condition is not required (no value) for operators IsNull, IsTrue and IsFalse; and it requires multiple values for In and ChildOf operator. For ChildOf operation three values are required in a specific order containing ParentEntityName, ParentIdFieldName andParentRecordId.
The join and join operator structures are used when querying across multiple entities. The join object structure while performing retrieve action that involves applying filter across different entities:
public class Join
{
public JoinOperator Operator { get; set; }
public string ToAlias { get; set; }
public string ToEntity { get; set; }
public string ToField { get; set; }
public string FromField { get; set; }
}
public enum JoinOperator
{
Inner = 0,
LeftOuter = 1,
RightOuter = 2,
}
The action response Output property is a generic object type as it contains different types of value for different actions. The actions and corresponding returned output type are –
• CreateRecord – string value containing the RecordId of the newly created record.
• UpdateRecord / DeleteRecord – empty string (also for any other action that does not return value)
• RetrieveRecord – Record object
• RetrieveMultipleRecords – Record[] (array of Record)
• RetrieveAttachmentList – Record (with a Field containing array of string having the file names)
• ExportData / ExportAttachment – Record (with a Field containing array of byte)
• RetrieveViewData / RetrieveStats – DataSheet (an object with a string Key mapped to a two dimentional string array to represent tabular data)
The response Output returned with Data request actions that denotes a dataset as a collection of key value pairs with a string for key mapping with a two dimensional string representing a tabular structure. The DataSheet mostly contains two tables named "Schema" and "Data" however custom actions can also return multiple tables with DataSheets containing different names. The DataSheets class is just a derivation of Dictionary with the following structure:
public class DataSheets : Dictionary<string, string[][]> { }
The connect action returns a session id that is required for invoking any subsequent action from the given user. As such the connect action can be invoked once and the session id returned from the action can be stored in the specific user context, this session id should then be set to action request for any other action being invoked by the user in the platform.
The connect action essentially takes three parameters (or fields) namely "DomainName", "UserName" and "Password" and returns session Id (string) as the response output. However the connect action is also required for Guest users (or when the user is not logged in), for this case the only required parameter is the "DomainName" (the UserName and Password fields are not passed for guest connection). The following code blocks shows getting a session Id for a user connection, just removing the UserName and Password fields from the Record object and specifying the fields array length as one will change it to return a guest connection session id.
ActionServiceClient _service = new ActionServiceClient();
Field[] credFields = new[]
{
new Field { Key = "DomainName", Value = "myDomainName" },
new Field { Key = "UserName", Value = "myUserName" },
new Field { Key = "Password", Value = "myPassword" }
};
Record input = new Record { EntityName = "Credential", Fields = credFields };
ActionRequest request = new ActionRequest { ActionName = "Connect", Input = input };
ActionResponse response = _service.Perform(request);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(response.ErrorMessage))
{
string sessionId = response.Output as string;
//store sessionId in user context for all subsequent action by the specific user
}
else
{
throw new Exception(response.ErrorMessage);
//connect action failed for the given credential
}
Following is another sample code that shows performing connect action through REST API –
StringBuilder requestBuilder = new StringBuilder();
requestBuilder.Append("{ \"ActionName\": \"Connect\", ");
requestBuilder.Append("\"Input\": { \"EntityName\": \"Credential\", ");
requestBuilder.Append("\"Fields\": [");
requestBuilder.Append("{ \"Key\": \"DomainName\", ");
requestBuilder.AppendFormat("\"Value\": \"{0}\" }}, ", "myDomainName");
requestBuilder.Append("{ \"Key\": \"UserName\", ");
requestBuilder.AppendFormat("\"Value\": \"{0}\" }}, ", "myUserName");
requestBuilder.Append("{ \"Key\": \"Password\", ");
requestBuilder.AppendFormat("\"Value\": \"{0}\" }} ", "myPassword");
requestBuilder.Append("] }}");//closing Fields array, Input and ActionRequest object
string erasPerformUrl = "http://eras.in/Host/service/perform";
HttpWebRequest http = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(new Uri(erasPerformUrl));
http.Accept = "application/json; charset=UTF-8";
http.ContentType = "application/json; charset=UTF-8";
http.Method = "POST";
Byte[] requestData = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(requestBuilder.ToString());
using (Stream reqStream = http.GetRequestStream())
reqStream.Write(requestData, 0, requestData.Length);
ActionResponse response;
DataContractJsonSerializer _deSerializer =
new DataContractJsonSerializer(typeof(ActionResponse));
using (WebResponse webRes = http.GetResponse())
using (Stream resStream = webRes.GetResponseStream())
response = _deSerializer.ReadObject(resStream) as ActionResponse;
//the response object returned has the following structure
[DataContract]
private class ActionResponse
{
[DataMember]
public string ErrorMessage { get; set; }
[DataMember]
public string Output { get; set; }
}
//the Output (string) property would contain the desired session id for connect action
Note: when establishing Guest connection the UserName and Password fields are NOT required. The following example shows creating such guest connection through JavaScript using REST/JSON API –
var _url = 'http://eras.in/Host/service/perform', _sessionId = null;
function getSessionId(async) {
var data = { EntityName: 'Credential' };
data.Fields = [{ Key: 'DomainName', Value: 'myDomainName' }];
var request = { ActionName: 'Connect' };
request.Input = data;
var strRequest = JSON.stringify(request);
var http = new XMLHttpRequest();
if (async) {
http.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (http.readyState == 4 && http.status == 200)
parseResponse(http);
};
}
http.open("POST", _url, async);
http.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=UTF-8");
http.setRequestHeader("Accept", "application/json; charset=UTF-8");
http.send(strRequest);
if (!async)
return parseResponse(http);
}
function parseResponse(http) {
var response = JSON.parse(http.responseText);
if (response.ErrorMessage != null && response.ErrorMessage != '') {
alert("Error : " + response.ErrorMessage);
return null;
}
_sessionId = response.Output;
return _sessionId;
}
The most commonly used actions available to all entities are listed below:
The CreateRecord action creates a record and returns the unique id (string) of the newly created record.
For this example let us assume an entity with Name "MyContact" is created and has attributes "FirstName" (single line, required, is lookup) and "ContactType" (option set, with options Friend, Family and Colleague)
ActionServiceClient _service = new ActionServiceClient();
Field[] dataFields = new[]
{
new Field { Key = "FirstName", Value = "Michael" },
new Field { Key = "ContactType", Value = "Friend" }
};
Record input = new Record { EntityName = "MyContact", Fields = dataFields };
ActionRequest request = new ActionRequest { ActionName = "CreateRecord", Input = input, SessionId = sessionId }; //sessionId from Connect action
ActionResponse response = _service.Perform(request);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(response.ErrorMessage))
{
string recordId = response.Output as string;
//recordId of the newly created record can be assigned to input.RecordId
}
else
{
throw new Exception(response.ErrorMessage);
//create record failed for the given input
}
Note: the same CreateRecord action can also be used to create entities, attributes, etc. by creating records of "System_Entity", "System_Attribute", etc. and passing the fields mapping with their respective attributes. Example for creating "System_Entity" we need to pass "SystemName", "DisplayName", "PluralDisplayName", "MainSiteOrder" (with value greater than or equal to 1 for it to be visible in MainSite).
The UpdateRecord action updates the record with the given record id. It is almost the same as CreateRecord action however only the fields required to be updated needs to be passed and the input record should have RecordId assigned.
Using the same example as CreateRecord we would update the ContactType for a specific record.
ActionServiceClient _service = new ActionServiceClient();
Field[] dataFields = new[]
{
new Field { Key = "ContactType", Value = "Colleague" }
};
Record input = new Record { EntityName = "MyContact", Fields = dataFields, RecordId = recordId }; //recordId is required
ActionRequest request = new ActionRequest { ActionName = "UpdateRecord", Input = input, SessionId = sessionId }; //sessionId from Connect action
ActionResponse response = _service.Perform(request);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(response.ErrorMessage))
{
//empty string returned in response.Output in case of UpdateRecord action
}
else
{
throw new Exception(response.ErrorMessage);
//update record failed for the given input
}
Note: when updating lookup type attribute, the corresponding related entity'srecord id must be assigned to that field.
The DeleteRecord action deletes the corresponding record based on given record id. This action does not require any fields to be passed just the record Id is required.
ActionServiceClient _service = new ActionServiceClient();
Record input = new Record { EntityName = "MyContact", RecordId = recordId }; //recordId is required
ActionRequest request = new ActionRequest { ActionName = "DeleteRecord", Input = input, SessionId = sessionId }; //sessionId from Connect action
ActionResponse response = _service.Perform(request);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(response.ErrorMessage))
{
//empty string returned in response.Output in case of DeleteRecord action
}
else
{
throw new Exception(response.ErrorMessage);
//delete record failed for the given input
}
The RetrieveRecord action retrieves a single record by id or by system name.
ActionServiceClient _service = new ActionServiceClient();
Field[] dataFields = new[]
{
new Field { Key = "Columns", Value = "FirstName,ContactType" }
};
Record input = new Record { EntityName = "MyContact", RecordId = recordId, Fields = dataFields}; //recordId is required
ActionRequest request = new ActionRequest { ActionName = "RetrieveRecord", Input = input, SessionId = sessionId }; //sessionId from Connect action
ActionResponse response = _service.Perform(request);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(response.ErrorMessage))
{
Record output = response.Output as Record;
//Record object returned in response.Output
}
else
{
throw new Exception(response.ErrorMessage);
//delete record failed for the given input
}
Note: for retrieving record by system name the entity must have a unique attribute with SystemName set to "SystemName", in such case the RetrieveRecord action can be called without setting the RecordId but with Fields containing a field with key "SystemName" and value corresponding to the unique value of SystemName for the required record.
The RetrieveMultipleRecords action retrieves multiple records (as array of record) based on query. This action is similar to RetrieveRecord action except it is used to retrieve multiple records and if required also based on some filter criteria.
For this example we will assume retrieving MyContact records with corresponding values for FirstName and ContactType and that has ContactType set to "Colleague".
ActionServiceClient _service = new ActionServiceClient();
Condition condition = new Condition { FieldName = "ContactType", Operator = ConditionOperator.Equal, Values = new object[] { "Colleague" } };
Filter filter = new Filter { Conditions = new[] { condition } };
Field[] dataFields = new[]
{
new Field { Key = "Columns", Value = "FirstName, ContactType" },
new Field { Key = "Filter", Value = filter }
};
Record input = new Record { EntityName = "MyContact", Fields = dataFields };
ActionRequest request = new ActionRequest { ActionName = "RetrieveMultipleRecords", Input = input, SessionId = sessionId };
ActionResponse response = _service.Perform(request);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(response.ErrorMessage))
{
Record[] output = response.Output as Record[];
//Record array is returned in response.Output
}
else
{
throw new Exception(response.ErrorMessage);
//create record failed for the given input
}
Note 1: The retrieve multiple record action also supports Get functions with Lookup type columns. For example the MyContact entity has a lookup type attribute CompanyId that relates it to another entity named MyCompany. In this case passing the columns key as –
new Field { Key = "Columns", Value = "FirstName, ContactType, CompanyId" }
Would yield in output records containing field named CompanyId with corresponding MyCompany entity'srecord id, which of course can be used to retrieve the details of the related company, but if just the related company'sunique display field (is lookup attribute, such as CompanyName) value is desired, the columns passed with the query can be-
new Field { Key = "Columns", Value = "FirstName, ContactType, Get_Text_CompanyId" }
In this case the returned record'swould contain a field with name Get_Text_CompanyId containing the unique lookup display field value (CompanyName).
Similar to the Get_Text is the Get_Name function; in case the MyCompany entity has an attribute named "SystemName", and the SystemName value of the corresponding company’s record is desired then the columns passed with query can contain Get_Name_CompanyId.
Note 2: The retrieve multiple record action also has optional parameters OrderBy, PageSize and PageCount which can be used along with filter to retrieve a specific paged set of records.
Note 3: It is also possible to build more complex queries along with Joins to retrieve records based on filters that are joined with other entities for example if we want to retrieve MyContact records that has ContactType "Colleague" and are related to MyCompany entity that has name set to "South Wind" then we can create filter and join as follows –
ActionServiceClient _service = new ActionServiceClient();
Condition conditionType = new Condition { FieldName = "ContactType", Operator = ConditionOperator.Equal, Values = new object[] { "Colleague" } };
Condition conditionComp = new Condition { FieldName = "Comp.CompanyName", Operator = ConditionOperator.Equal, Values = new object[] { "South Wind" } };
Filter filter = new Filter { Operator = FilterOperator.And,
Conditions = new[] { conditionType, conditionComp } };
Join joinComp = new Join { ToEntity = "MyCompany", ToAlias = "Comp",
ToField = "Comp.MyCompanyId", FromField = "CompanyId"};
Field[] dataFields = new[]
{
new Field { Key = "Columns", Value = "FirstName, ContactType" },
new Field { Key = "Filter", Value = filter },
new Field { Key = "Joins", Value = new[] { joinComp } }
};
Record input = new Record { EntityName = "MyContact", Fields = dataFields };
ActionRequest request = new ActionRequest { ActionName = "RetrieveMultipleRecord", Input = input, SessionId = sessionId };
ActionResponse response = _service.Perform(request);
The resulting response would contains Output as array of Records of MyContact entity which has ContactType equal to "Colleague" and are related to company "South Wind".
1. UploadAttachment – attaches a file to the record.
2. DownloadAttachment – retrieves a file attached to record.
3. RetrieveAttachmentList – retrieves the list of files attached to record.
4. DeleteAttachment – deletes a file from the record'sattachments.
5. DeleteAllAttachments – deletes all files attached to the record.
1. ImportData – Imports records from comma separated (csv) file into the corresponding entity.
2. ImportAttachments – Imports attachments from zip file and attaches them to corresponding records.
1. ExportData – Exports records as comma separated (csv) file from any given entity
2. ExportAttachments – Exports attachments of records into a zip file from any given entity.
Note: there are also Data Actors like RetrieveStats, RetrieveViewData, RetrieveRelationInfo, RetrieveAccessInfo, etc. which are associated with all entities, however these are designed for programmatic access and are detailed in Eraspaas Programming Guide.
Some of the common entity specific actions are ImportSolution, ExportSolution, ImportSiteContent, ExportSiteContent, ReceiveEmails, ViewReport etc. which are available from corresponding entities views more actions dialog.
Some of the common "On Event" actions are Table Actors like CreateTable, CreateColumn, UpdateColumn etc. which gets triggered when Entity or Attribute records are created. SendEmail when record of Email is created or updated with Email State as "Send".
The import solution action allows importing Eraspaas solution into a domain and can also be performed programmatically:
The send email action allows sending email from Eraspaas domain. It is performed by creating email record with EmailState field set to "Send" or can also be used to send already created email by updating the EmailState field of the corresponding record to "Send".
Eraspaas service can also invoke external actions (or service) that are available over standard web API over https and http protocols. For this the ActionPath value in the corresponding Action record should be set to a public internet url such as http://myserverOrIP/Servlet.svc
10.1 Transform Format and Transform Definition
By default the Record object that is passed while triggering the action is serialized and passed to the external action; however it is possible to change the structure of the input, by providing custom xml or json string or plain text with placeholders that will be replaced with the corresponding input record field values. For example for an action a record object is passed with two fields having keys "SystemName" and "DisplayName" and corresponding values in the value of the field. And this information is to be passed to an external action in custom xml format which is understood by the external action such as:
<Input>
<SystemName>(@SystemName)</SystemName>
<DisplayName>(@DisplayName)</DisplayName>
</Input>
Then this value must be provided to the Transform Definition field. Similarly if using json format, then the Transform Definition value can be -
{"SystemName": (@SystemName), "DisplayName": (@DisplayName)}
The format of the place holder is (@FieldKey) including the brackets. Apart from the fields that are passed through the input record, it is also possible to pass server context values by specifying placeholders in the format ($$ServerValueKey) for example: ($$CurrentUser), ($$CurrentDepartment), ($$CurrentDateTime), ($$CurrentDate), ($$CurrentDomain).
Note: It is also possible to have such placeholders in the actor path, for instance like passing values in query string to external action.